About the Project
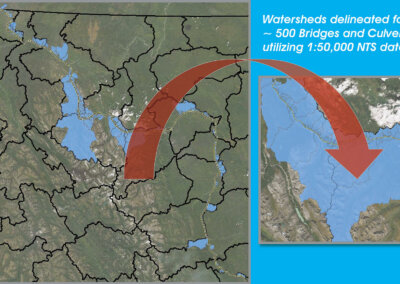
Public Services Procurement Canada teamed with Tetra Tech Canada Inc. (Tetra Tech) to develop a multi-disciplinary study on the Infrastructure Vulnerability and Risk Assessment due to Changing Climate and Extreme Weather Events for the Alaska Highway. The project posed many unique challenges, including the incorporation of 410 selected culverts across 361 sites, 74 geotechnical assets, and 24 bridges into the asset decision-making framework.
The project needed an innovative approach for compiling and assessing the variety of asset components (asset type, location, and condition), and then incorporating a decision-making schema that could prioritize asset replacement – Accounting for asset condition and vulnerability, while considering the potential effects of climate change.
The project team’s approach was unique in that it adopted the methodology documented under the Vulnerability Assessment and Adaptation Framework developed by Federal Highway Administration, which provides a process for conducting a vulnerability assessment for the infrastructure assets. The approach expanded on a method previously developed by Tetra Tech and the US Army Corps of Engineers. This method is based on “risk-based asset management” fundamentals. The approach incorporated a means for assessing and forecasting the risk, or probability of failure, of each individual asset, and assessed the consequence in dollars of the potential failure.
When applied to all Alaska Highway transportation assets, this approach provides a quantitative cost-benefit (or cost risk) measure without any of the bias that often influences asset replacement decision making (bridges are more important than roads, for example). The outcome was a detailed priority ranking of all of the corridor’s assets, where asset replacement is categorized by benefit/cost. This approach results in a genuinely optimal asset management plan, allowing for asset replacement planning based on an informed decision-making process.
Approach
The Infrastructure Vulnerability Assessment was carried out using the methodology documented under the FHWA, 2017 (the Framework). The Framework provides an in-depth and structured process for conducting a vulnerability assessment for the infrastructure assets. The work for this project included the completion of the steps described in the Framework.
The Framework describes several steps involved in conducting a vulnerability assessment. The methodology adopted to complete each step is provided in the steps below.
- Step 1: Articulate Objectives and Scope
- Step 2: Obtaining Asset Data
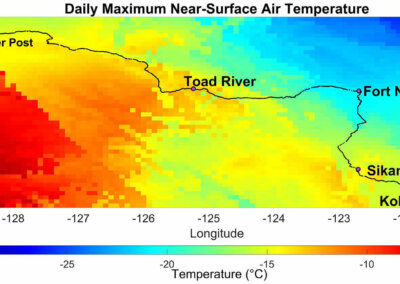
- Step 3: Obtaining Climate Data
- Step 4: Assessment of Vulnerability
- Step 5: Identify, Analyze and Prioritize Adaptation Options
- Step 6: Incorporate Assessment Results in Decision making
- Step 7: Monitor and Revisit
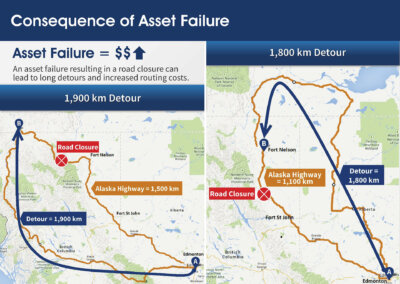
The non-conventional approach used objective parameters such as traffic, detour length, agency consequence, user consequence, etc., to minimize the role of heuristic bias and uncertainty in engineering judgement in traditional approaches.
A significant innovation was that the cost/benefit of adding resiliency to Changing Climate and associated Extreme Weather Events is both forecasted and included in the engineering economics-based Life-Cycle Cost Analysis.
This unique solution is possibly the first implementation of its kind relating to a transportation corridor – combining a monetized risk-and-reliability/climate change vulnerability asset management program.
Results
The engineering economics informed vulnerability assessment of assets showed that the savings in reduced risk out weighed the costs of adding resiliency at several sites. At one site, the savings in reduction in risk was nine times the cost of the added resiliency. At a further 38 sites, the savings in reduced risk out weighed the cost of the added resiliency. The results show that these assets may be vulnerable and a site-level investigation should be carried out to confirm the analysis.
Service(s) Provided
Weather related science/meteorology;
• Roadway Asset Inventory and Condition Data collection;
• Terrain Modeling;
• Hydraulic Engineering;
• Geotechnical Engineering;
• Transportation Engineering;
• Asset Management.
Go back to projects in
View other projects from
Stay in touch with us
Subscribe to our mailing list!
Organization
Connect